
Understanding Networking Concepts through Cisco Packet Tracer
Networking is one of the most important aspects of modern IT. It connects devices, enables communication, and ensures everything from browsing the internet to file sharing works seamlessly. Throughout my time in the Computer Systems Technician program at St. Lawrence College (SLC), I’ve learned the fundamentals of networking, and using Cisco Packet Tracer has been a huge part of that learning process. This tool has helped me simulate real-world networks and apply theoretical knowledge in a way that feels tangible and practical.
Theoretical Knowledge Gained in Networking
When it comes to networking, one of the first things I learned was the importance of IP addressing. IP addresses act as the unique identifiers for devices within a network, ensuring they can send and receive data correctly. Learning how IPv4 and IPv6 addresses differ has been essential for me to understand how networks evolve and how they scale over time. I’ve also learned to configure both static and dynamic IP addresses, which play a critical role in ensuring that devices can connect properly and communicate.
Another idea I studied was subnetting, which involves dividing a big network into smaller, more manageable portions. While this initially seems difficult, I now understand how subnetting helps networks run more efficiently by minimizing traffic congestion. Understanding subnetting allows me to verify that data flows properly across various regions of the network. The OSI model also helped me comprehend how data moves across networks. This seven-layer approach is important because it breaks down each level of data transfer, allowing me to troubleshoot problems and pinpoint where they may be occurring.
Using Cisco Packet Tracer to Simulate Networks
Cisco Packet Tracer has been one of the most effective tools in helping me apply everything I’ve learned. It’s a network simulation software that lets me create virtual networks and configure devices like routers, switches, and computers. One of the most rewarding aspects of using Packet Tracer is the ability to set up networks and see them in action. I could design a network, assign IP addresses, configure routing protocols, and test how the data moves through the system.
Packet Tracer also allowed me to troubleshoot network issues in a virtual environment, which is particularly valuable since it provides a safe space to experiment without any real-world consequences. For example, I could simulate a cable being unplugged, a router misconfiguration, or a network going down, and then try to fix it. This hands-on approach helped me not only better understand networking but also feel confident in my ability to resolve problems when they arise in actual networks.
Understanding Network Topologies
Network topologies are essentially the layout of how devices are connected within a network. The structure of a network has a big impact on its performance, scalability, and reliability. I explored several topologies during my studies, such as the star, mesh, and bus topologies.
In a star topology, all devices are linked to a main hub, and it becomes simpler to diagnose as if one device fails, others will not be affected. But if the central hub is destroyed, the entire network fails. A mesh topology offers higher redundancy. Each device is connected to every other device, so the network becomes more reliable but more complicated and expensive. I could experiment with these topologies in Packet Tracer, and I could observe their impact on network reliability and performance.
Understanding Network Security
Security is an essential part of networking, as it protects the network and its data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. I’ve learned about the importance of firewalls, encryption, and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs).
The Firewall is like the gatekeeper, it permits the legitimate traffic but blocks all the unwanted and suspicious traffic. Through configuring firewalls, I was able to gain hands on knowledge on establishing traffic rules that govern data based on criteria to protect the network. Encryption is another critical security layer-it makes sure that any data transmitted through the network is encrypted and unreadable to whoever intercepts it. Lastly, VPNs provide a secure communication channel between a user and a private network via the internet, protecting sensitive information even when transmitted over unprotected mediums.
In Packet Tracer, I practiced implementing these security measures, helping me understand how each layer of protection works to safeguard networks and data from cyberattacks.
The Role of DNS in Networking
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a fundamental part of how the internet works. DNS acts like a phonebook, translating human-readable domain names (such as www.example.com) into machine-readable IP addresses. Without DNS, we would have to remember and type in long numerical addresses to access websites, which would be inconvenient at best.
I learned how DNS servers are configured and how they work to ensure that devices can find each other on the network. In Packet Tracer, I simulated the DNS process, setting up DNS servers and observing how they translate domain names into IP addresses. This helped me realize how crucial DNS is in making the internet user-friendly and efficient.
The Role of Networking in IT
Networking is the backbone of IT. Without networks, devices would be isolated, unable to communicate with each other or access shared resources. Throughout my studies, I’ve learned that networking skills are essential for nearly every role in IT. Whether you’re managing network infrastructure, troubleshooting connectivity issues, or setting up secure networks, understanding networking concepts is key.
Even though I’ve only worked with virtual networks using Packet Tracer, the knowledge I’ve gained has prepared me for working with real-world network environments. As I move forward in my career, I know that networking will be an area I’ll continue to build upon, whether I’m supporting end-users, working as a network administrator, or managing enterprise-level systems.
Skills Developed & Challenges Overcome
One of the biggest challenges I encountered was subnetting. At first, it felt like an overwhelming concept because it required a lot of calculation and understanding of binary math. However, with continued practice and by using tools like Packet Tracer, I became more comfortable with subnetting and could confidently divide networks into subnets.
Troubleshooting network issues was another area where I faced challenges. It wasn’t always easy to identify the source of the problem, especially when dealing with complex configurations. However, by using Packet Tracer’s simulation tools, I was able to systematically work through issues, check configurations, and test solutions. This experience taught me to approach problems methodically and patiently, skills that will serve me well in the future.
Conclusion
Through my courses and work with Cisco Packet Tracer I’ve built a strong foundation in networking. I’ve learned everything from understanding IP addressing and subnetting to exploring network security and DNS, invaluable skills I will continue to build on. This practical exposure, especially through Cisco Packet Tracer, has helped me translate theoretical knowledge into tangible skills, allowing me to tackle real-world networking problems with confidence. In the future, while developing my career, I wish to strengthen my knowledge more and apply these skills to design, secure, and manage the networks in the best possible way.
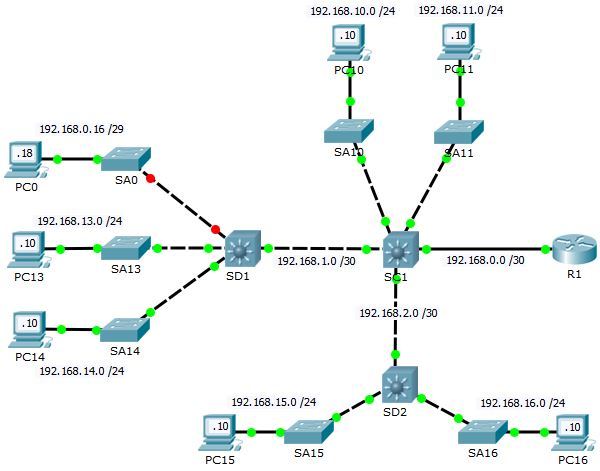
An Image showing an example of Cisco Packet Tracer Configuration
Leave a Reply